
Areas most affected by cutaneous horns. Cutaneous horn may arise from a wide range of the epidermal lesions which may be benign premalignant or malignant.
J Clin Microbiol 49 2 707-709 PubMed.
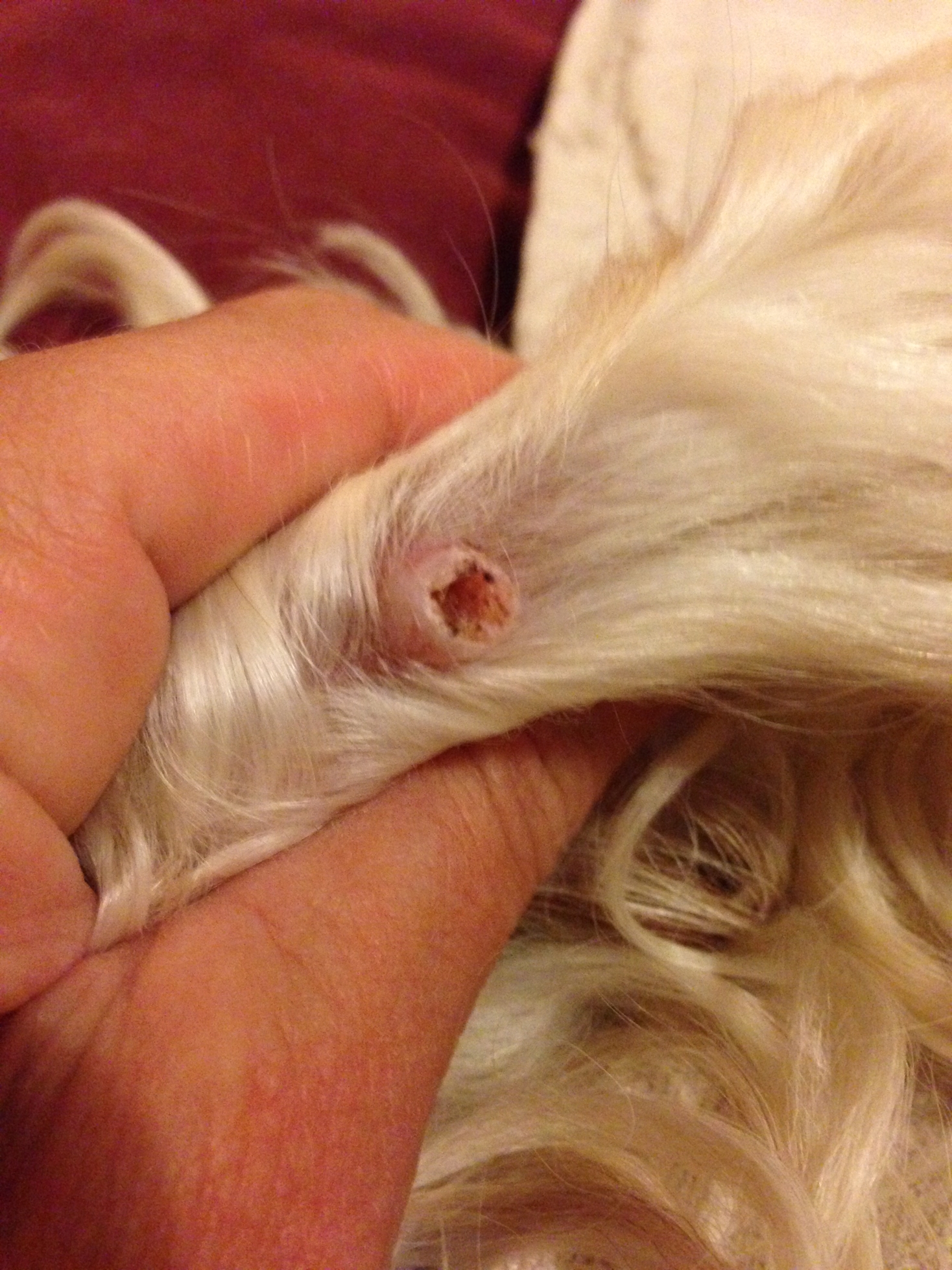
Cutaneous horn on dog. Furthermore what is a cutaneous horn in dogs. The cutaneous horns are projections cornified composed of keratin similar to horns of animals. They are usually associated with benign lesions which may or may not be concomitant skin lesions.
The diagnosis relies on surgical resection of the lesion and histopathological evaluation. Should you remove a cutaneous horn on dog. Another growth called a keratoacanthoma can develop from a cutaneous horn though this is rare.
This type of growth is relatively common and often benign. A doctor may recommend surgical removal to reduce the risk of a keratoacanthoma becoming malignant as it can resemble squamous cell carcinoma. The cutaneous horns are projections cornified composed of keratin similar to horns of animals.
They are usually associated with benign lesions which. Areas most affected by cutaneous horns. A dogs chest tail back and legs are the areas most affected by cutaneous horns growth.
This nail-like condition may also develop on a dogs footpads looking like an extra nail growing in the wrong place. See also Nail Bed Cancer In Dogs Symptoms Diagnosis Solution. Less often cutaneous horns form in dogs as a result of a canine papillomavirus infection.
Symptoms A doctor can often diagnose a cutaneous horn. A cutaneous horn on a dog will be a growth that sticks up from the skin surface. It can feel like a stick-like growth on a dogs tail.
While they can develop anywhere they often appear on the back tail and legs. Cutaneous horns cornu cutaneum are uncommon lesions consisting of keratotic material resembling that of an animal horn. Cutaneous horn may arise from a wide range of the epidermal lesions which may be benign premalignant or malignant.
Discussion Starter 1 Jan 13 2015. Only show this user. I recently discover a black nail like horn on my dogs paw pad which is called cutaneous horn it growed so fast that i just cant believe myself how i couldnt notiece it until know anyone elses dog suffered this.
How dangerous can it be. Cutaneous horns typically affect the paw pads. While you can remove them theyll often regrow unless the entire mass including the base is removed.
This is often difficult though since that sometimes requires creating a large defect in the pad. A cutaneous horn is a type of lesion or growth that appears on the skin. Its made of keratin which is a protein that makes up the top layer of the skin.
The growth may look like a. A cutaneous horn generally presents as a straight or curved hard yellow-brown projection from the skin. It can be surrounded by normal skin or have a border of thickened skin.
The side of the horn may be terrace-like or oyster shell-like with horizontal ridges. The base of the horn may be flat protruding or like a crater. Magoo has come to Critter Fixer with an unusual skin growth - cutaneous horn.
HttpbitlyNatGeoWILDSubscribe Get more Critter. Animal horn that ranges in size from a few millime-ters to several centimeters 9. Cutaneous horns are uncommon tumors in dogs 2 and the few existing reports are brief.
Diagnosis is made by appearance course of injury and biopsy 6 which must include tumors hyperkeratotic base where primary benign or malignant lesions may be present 3. They may be seen in dogs of any age but occur most commonly in dogs 8 to 10 years old. They may develop anywhere on the body surface as well as in internal organs but the limbs especially the back of the upper thigh lower abdomen and chest are the most common sites.
Papillomas can cause the development of cutaneous horns and potentially this claw alteration was linked to the skin disease. Neoplasia of the nail fold is a common cause of onyxis and onychomadesis in the old dog. Squamous cell carcinoma which is often misleading since it looks like a non-healing wound melanoma and mast cell tumour are.
Cutaneous horns also known by the Latin name cornu cutaneum are unusual keratinous skin tumors with the appearance of horns or sometimes of wood or coral. Formally this is a clinical diagnosis for a conical projection above the surface of the skin They are usually small and localized but can in very rare cases be much larger. Although often benign they can also be.
A cutaneous horn is a cone-shaped lesion on the skin that grows straight outward and looks very much like a small horn. In some cases it is a benign growth but in others it may be pre-cancerous or cancerous. Cutaneous horns are uncommon lesions made of compact keratin.
They resemble an animals horn. They can occur anywhere on the body but are mostly seen in sun-exposed areas like the face ear nose forearms and hands. Though 60 of the cutaneous horns are non-cancerous some may turn cancerous too.
Lange C E Zollinger S Tobler K et al 2011 Clinically healthy skin of dogs is a potential reservoir for canine papillomaviruses. J Clin Microbiol 49 2 707-709 PubMed. Munday J S French A F MacNamara A R 2010 The development of multiple cutaneous inverted papilloma following ovariohysterectomy in a dog.
NZ Vet J 58 3 168-171 PubMed. A cutaneous horn is a conical projection of hyperkeratotic epidermis. Though grossly resembling an animal horn it lacks a bony core.
These lesions have been well described in. Basal cell tumors represent a heterogeneous group of cutaneous epithelial neoplasms recognized most commonly in cats less commonly in dogs occasionally in horses and sheep and seldom in other domestic animals. These neoplasms are composed of a proliferation of small basophilic cells that exhibit morphology reminiscent of the progenitor cells of the epidermis and adnexa.
This is the first thoroughly documented case of canine CHs associated with PV infection in a fiveyear-old castrated male pit bull dog and the associated virus was identified as CPV1. Cutaneous horns CHs are conical hyperkeratotic cutaneous protrusions that appear similar to animal horns but lack bone. The term cutaneous horn is a morphological description not a.